Colour is a universal language that speaks to our emotions and perceptions and influences our behaviour. In the vast realm of design, whether for art, fashion, or branding, understanding colour theory is like having a secret key to unlock a world of possibilities.
The Basics of Colour Theory:
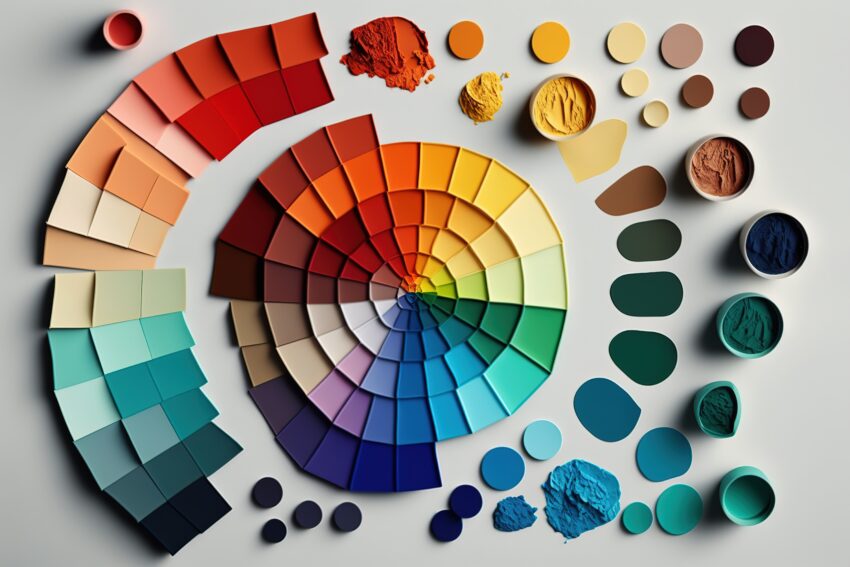
- The Colour Wheel: The colour wheel is at the heart of colour theory, a circular diagram that organises colours based on their relationships. Primary colours (red, blue, and yellow) form the foundation and secondary and tertiary colours emerge as combinations.
- Colour Harmony: Colour harmony involves combining colours in a visually appealing way. Common harmony schemes include complementary, analogous, triadic, and tetradic colour combinations. Each scheme imparts a distinct mood and balance to a design.
The Psychology of Colour:
- Emotional Impact: Colours have the power to evoke emotions. For instance, warm colours like red and orange often convey energy, passion, and warmth, while cool colours like blue and green evoke calmness and tranquillity. Understanding these emotional responses is crucial in design and branding.
- Cultural Influences: Colours can have different meanings across cultures. Red, for example, symbolises luck in Chinese culture but can signify danger or warning in Western cultures. Being aware of cultural associations ensures designs resonate positively with diverse audiences.
Practical Applications:
- Branding and Marketing: Companies strategically use colour to establish brand identity and connect with their target audience. Think about iconic brands like Coca-Cola with its bold red or the calming blue of Facebook – each colour is chosen to convey a specific message.
- Web and Graphic Design: In web and graphic design, colour choices impact user experience. Well-thought-out colour schemes improve readability, draw attention to important elements, and guide users through a seamless journey.
- Interior Design: Colour theory plays a pivotal role in interior design, influencing the ambience of a space. Warm colours can make a room feel cosy, while cool colours open up and brighten a space. Interior designers use colour to create harmonious and inviting environments.
Colour in Art:
- Expressive Possibilities: Artists use colour to convey mood, emotion, and meaning in their work. Techniques like colour contrast and saturation add depth and dimension to paintings. For instance, Vincent van Gogh’s use of vibrant yellows in “Sunflowers” exudes energy and optimism.
- Symbolism in Art: Colours are often symbolic in art. For example, using gold in religious paintings signifies divinity, while darker colours might convey sombre or mysterious themes.

Van Gogh Museum, Amsterdam, Netherlands.
Colour theory is a rich and dynamic field that transcends mere aesthetics; it’s a powerful tool that communicates, resonates, and leaves a lasting impression. Whether you’re a designer, artist, marketer, or simply someone interested in the visual world, understanding colour theory opens up a realm of possibilities, allowing you to harness the true potential of every hue on the spectrum.



